Working across the supply chain to reduce scope 3 emissions
Scope 3 emissions make up around 95% of Nutreco’s total GHG emissions. Since these emissions are outside of our direct control, we created a dedicated scope 3 reduction program, based on three reduction strategies, and supported by an internal engagement program.
Strategy one: Supplier engagement
The first strategy is supplier engagement. We actively reach out to select suppliers to engage them on our journey. Our discussions cover: (1) their available supplier-specific footprint data, to help us get a better understanding of where they are in the emissions-reduction process and increase confidence in our baseline calculations, (2) their commitment to the SBTi, and (3) their approach and maturity on the topics of climate and circularity.


Strategy two: Lower footprint ingredients
During our discussions with suppliers, we also request that they share primary emissions data, for example, LCA data for specific products they deliver. This will help us to better understand emissions across the supply chain and achieve our second reduction strategy: selecting low-emissions ingredients. When similar ingredients come with different footprints, we give preference to the ingredients with the lowest footprints – including alternative ingredients, such as by-products, and circular ingredients, including single-cell proteins or insect-based raw materials.
Strategy three: Land-use change
Our third reduction strategy is related to land-use change, the biggest driver of our scope 3 GHG emissions. Land transformation by human activities is often related to the release, or decreased sequestration, of GHGs. In particular, deforestation to free up space for the cultivation of vegetable ingredients is significantly driving up the land-use change part of our emissions. By working together with our suppliers to combat deforestation, we will reduce the land-use change associated with our ingredients and, with it, the GHG emissions associated with our feeds. Certification, particularly focused on soy and oil palm, also plays a significant role in reducing this share of our footprint.

Our progress
We created a specialist team to strengthen our LCA platform and tackle the scope 3 science-based targets we have set. We launched a new marine sourcing policy, describing in an open and transparent way, as we did for soy and oil palm, our expectations around sourcing marine products and providing a step plan for our Purchasing team
Because Nutreco sources raw materials from many suppliers all over the world, it is impossible to engage with all of them in an effective way. We use secondary data, such as average LCA data from recognised LCA databases, to identify the ingredients and suppliers that contribute the most to our scope 3 emissions. We found that 216 ingredient suppliers account for 80% of our scope 3 emissions, so we focus on these suppliers, engaging with them to identify potential GHG emissions-reduction opportunities.
Nutreco is part of a growing group of companies setting ambitious GHG-reduction targets for 2030, and we will ask our suppliers to do the same. By increasing the share of suppliers committed to science-based targets, we hope to increase the LCA knowledge across the whole value chain.
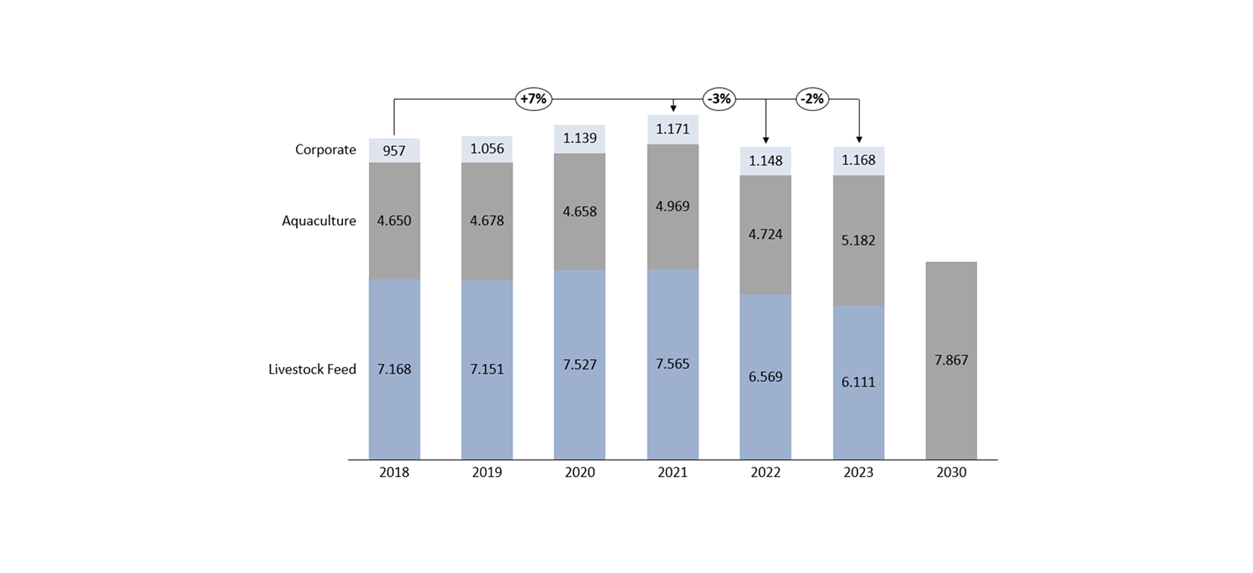
The decrease in our scope 3 emissions over the full year was mainly due to a slight reduction in our volume and different formulation choices such as changes in raw material sourcing to low footprint alternatives.
Nutreco’s scope 3 emissions:
Life Cycle Assessment – the most comprehensive method to quantify environmental impactTo fulfil one commitment outlined in Nutreco’s Roadmap 2025, Nutreco stepped up in developing and implementing Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)-based metrics. “Life Cycle Thinking” means that all stages of a product’s life cycle are considered, meaning not only direct emissions or resource extraction happening on site, but also indirect environmental impacts further upstream or downstream. It also quantifies all relevant potential environmental impacts caused by the object being studied. Today, we often focus on climate impacts as the most urgent environmental problem to solve. However, there are also other environmental impacts that can be quantified with the LCA method, that may be overlooked when only focusing on, for example, the carbon footprint. We are already overshooting these boundaries on a global scale, which increases the “risk of large-scale abrupt or irreversible environmental changes” (SRI, 2022). At Nutreco, we acknowledge these planetary boundaries. While we focus on carbon footprinting, we also try to consider other environmental impacts when developing our carbon-reduction strategies. The implementation of LCA-based metrics into our systems helps us on this learning journey. |